A cosmic holiday ornament, Hubble-style

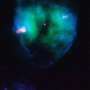
(Phys.org)—'Tis the season for holiday decorating and tree-trimming. Not to be left out, astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have photographed a festive-looking nearby planetary nebula called NGC 5189. The intricate structure of this bright gaseous nebula resembles a glass-blown holiday ornament with a glowing ribbon entwined.
Planetary nebulae represent the final brief stage in the life of a medium-sized star like our Sun. While consuming the last of the fuel in its core, the dying star expels a large portion of its outer envelope. This material then becomes heated by the radiation from the stellar remnant and radiates, producing glowing clouds of gas that can show complex structures, as the ejection of mass from the star is uneven in both time and direction.
A spectacular example of this beautiful complexity is seen in the bluish lobes of NGC 5189. Most of the nebula is knotty and filamentary in its structure. As a result of the mass-loss process, the planetary nebula has been created with two nested structures, tilted with respect to each other, that expand away from the center in different directions.
This double bipolar or quadrupolar structure could be explained by the presence of a binary companion orbiting the central star and influencing the pattern of mass ejection during its nebula-producing death throes. The remnant of the central star, having lost much of its mass, now lives its final days as a white dwarf. However, there is no visual candidate for the possible companion.
The bright golden ring that twists and tilts through the image is made up of a large collection of radial filaments and cometary knots. These are usually formed by the combined action of photo-ionizing radiation and stellar winds.
This image was taken with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 on October 8, 2012, in filters tuned to the specific colors of fluorescing sulfur, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Broad filters in the visible and near-infrared were used to capture the star colors.
Provided by ESA/Hubble Information Centre