Last update:
Computer Sciences news

All the right moves in martial arts: Researchers develop system to quickly identify errors and improve form
Research in the International Journal of Biometrics introduces a new method for assessing a practitioner's precision in martial arts training. The method focuses on quickly identifying errors in the athlete's movements and ...
Engineering
20 hours ago
0
5

Team develops efficient stochastic parallel gradient descent training for on-chip optical processors
A new publication in Opto-Electronic Advances discusses efficient stochastic parallel gradient descent training for on-chip optical processors.
Electronics & Semiconductors
May 1, 2024
0
11

Researchers conduct survey on deduplication systems
A review published in the International Journal of Grid and Utility Computing has investigated ways in which the increasing problem of duplicate data in computer storage systems might be addressed. Solutions to this problem ...
Computer Sciences
May 1, 2024
0
6

A new framework to improve high computing performance
From a luxury to a day-to-day necessity, computing isn't quite what it used to be. As applications like machine learning and 5G mobile networks become the norm, the need for high computing performance has never been greater. ...
Computer Sciences
Apr 30, 2024
0
29
AI speech analysis may aid in assessing and preventing potential suicides, says researcher
Speech is critical to detecting suicidal ideation and a key to understanding the mental and emotional state of people experiencing it. Suicide hotline counselors are trained to quickly analyze speech variation to better help ...
Computer Sciences
Apr 30, 2024
0
24

Mathematical formulation of hazardous scenarios for automated driving systems
A research group including Professor Hasuo Ichiro of the Information Systems Architecture Science Research Division of the National Institute of Informatics, Dr. Waga Masaki, Assistant Professor of the Department of Informatics ...
Computer Sciences
Apr 29, 2024
0
0

Researchers develop a new way to instruct dance in virtual reality
Researchers at Aalto University were looking for better ways to instruct dance choreography in virtual reality. The new WAVE technique they developed will be presented in May at the CHI conference for human-computer interaction ...
Computer Sciences
Apr 29, 2024
0
29

Initiative encourages computer science students to incorporate ethics into their work
Computer science students at the University of Toronto are learning how to incorporate ethical considerations into the design and development of new technologies such as artificial intelligence with the help of a unique undergraduate ...
Computer Sciences
Apr 29, 2024
0
6

As quantum computers advance, encryption methods will need to keep up
Imagine the tap of a card that bought you a cup of coffee this morning also let a hacker halfway across the world access your bank account and buy themselves whatever they liked. Now imagine it wasn't a one-off glitch, but ...
Computer Sciences
Apr 29, 2024
0
3

Computer scientists unveil novel attacks on cybersecurity
Researchers have found two novel types of attacks that target the conditional branch predictor found in high-end Intel processors, which could be exploited to compromise billions of processors currently in use.
Computer Sciences
Apr 27, 2024
0
82

'POLAR' lowers the adoption barrier for adaptive query processing in database systems
The preprint "POLAR: Adaptive and Non-invasive Join Order Selection via Plans of Least Resistance" introduces an adaptive query processing technique that lowers the adoption barrier for existing database systems while decreasing ...
Computer Sciences
Apr 25, 2024
0
0

Adobe's VideoGigaGAN uses AI to make blurry videos sharp and clear
A team of video and AI engineers at Adobe Research has developed an AI application called VideoGigaGAN, that can accept a blurry video and enhance it to make it a much shaper product. The team describes their work and results ...

Research team accelerates multi-physics simulations with El Capitan predecessor systems
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have achieved a milestone in accelerating and adding features to complex multi-physics simulations run on Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), a development that could ...
Engineering
Apr 24, 2024
0
1
New tech could help traveling VR gamers experience 'ludicrous speed' without motion sickness
Vehicle passengers using VR headsets to pass the time during travel could be set to enjoy games which move at 'ludicrous speed' without experiencing motion sickness, researchers say.
Consumer & Gadgets
Apr 24, 2024
0
15

Emulating neurodegeneration and aging in artificial intelligence systems
In recent years, developers have introduced artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can simulate or reproduce various human abilities, such as recognizing objects in images, answering questions, and more. Yet in contrast ...

With a game show as his guide, researcher uses AI to predict deception
Using data from a 2002 game show, a Virginia Commonwealth University researcher has taught a computer how to tell if you are lying.
Computer Sciences
Apr 23, 2024
0
60
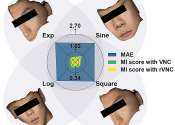
Coordinate-wise monotonic transformations enable privacy-preserving age estimation with 3D face point cloud
In a recent publication in Science China Life Sciences, a research team led by Professor Jing-Dong Jackie Han and Ph.D. student Xinyu Yang from Peking University established a deep learning model for age estimation using ...
Computer Sciences
Apr 23, 2024
0
1

New mitigation framework reduces bias in classification outcomes
We use computers to help us make (hopefully) unbiased decisions. The problem is that machine-learning algorithms do not always make fair classifications if human bias is embedded in the data used to train them—which is ...
Computer Sciences
Apr 23, 2024
0
0

Scientists revisit multi-dimensional classification from a dimension-wise perspective
While the class imbalance issue has been extensively investigated within the multi-class paradigm, its study in the multi-dimensional classification (MDC) context has been limited due to the imbalance shift phenomenon. A ...
Computer Sciences
Apr 23, 2024
0
1
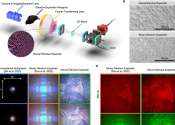
Holographic displays offer a glimpse into an immersive future
Setting the stage for a new era of immersive displays, researchers are one step closer to mixing the real and virtual worlds in an ordinary pair of eyeglasses using high-definition 3D holographic images, according to a study ...
Electronics & Semiconductors
Apr 23, 2024
0
53
More news
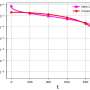
New logarithmic step size for stochastic gradient descent

Large language models generate biased content, warn researchers
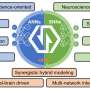
Advancing brain-inspired computing with hybrid neural networks

Brain-inspired computing may boil down to information transfer
Other news

Boeing's Starliner finally ready for first crewed mission
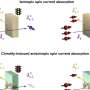
When injecting pure spin into chiral materials, direction matters

Lego-pushing bumblebees reveal insect collaboration dynamics
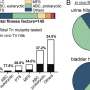
How E. coli get the power to cause urinary tract infections

Computer scientists show the way: AI models need not be so power hungry

DeepMind develops SAFE, an AI-based app that can fact-check LLMs
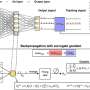
Brain-inspired chaotic spiking backpropagation
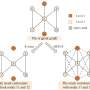
A biased edge enhancement method for truss-based community search

Q&A: How to train AI when you don't have enough data

Artificial intelligence boosts super-resolution microscopy

Chemist explores the real-world science of Star Wars
Novel triple drug combination effective against antibiotic-resistant bacteria